Anaerobic bacteria are microorganisms that grow in oxygen-free environments and play significant roles in human health and disease. In clinical settings, they are commonly associated with infections such as abscesses, soft tissue infections, and post-surgical complications.
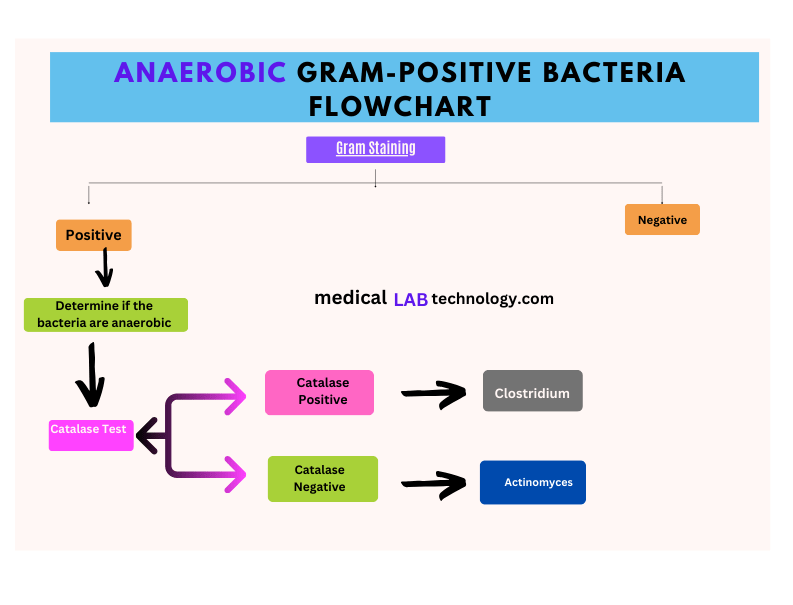
Anaerobic Gram-Positive bacteria flowchart
Here is the Flowchart for anaerobic Gram-positive bacteria for identification and differentiation.
- Sample Collection: Obtain the bacterial sample.
- Gram Staining: Perform Gram staining to confirm the bacteria are Gram-positive.
- Oxygen Requirement Test: Determine if the bacteria are anaerobic (grow in the absence of oxygen).
- Catalase Test: Determine if the bacteria produce the enzyme catalase.
- Catalase Positive: Possible genera include Clostridium, Lactobacillus, etc.
- Catalase Negative: Possible genera include Actinomyces, Propionibacterium, etc.
- Biochemical Tests: Other test like sugar fermentation, gas production, etc., can be needed to narrow down the specific genus and species.
Anaerobic Gram-Positive bacteria Examples
- Clostridium spp.: Causes tetanus, botulism, gas gangrene, and C. difficile-associated colitis.
- Peptostreptococcus spp.: Found in polymicrobial infections, including dental abscesses.
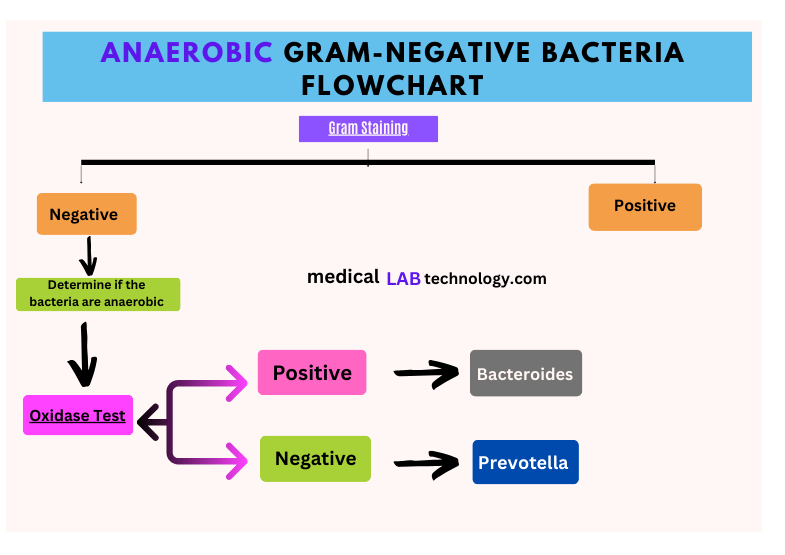
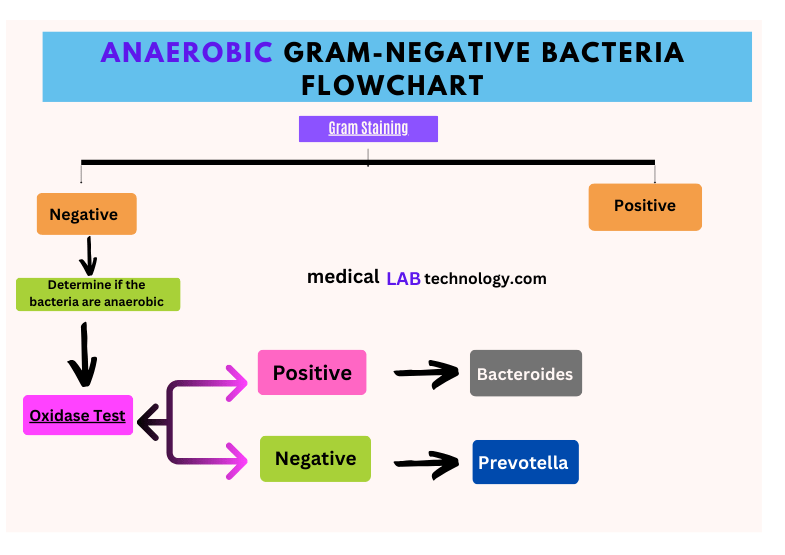
Anaerobic Gram-Negative bacteria flowchart
Here is the Flowchart for identifying anaerobic Gram-negative bacteria.
- Sample Collection: Obtain the bacterial sample.
- Gram Staining: Confirm the bacteria are Gram-negative.
- Oxygen Requirement Test: Determine if the bacteria are anaerobic (grow in the absence of oxygen).
- Oxidase Test: Check if the bacteria produce the enzyme oxidase.
- Oxidase Positive: Possible genera include Bacteroides, Fusobacterium, etc.
- Oxidase Negative: Possible genera include Prevotella, Porphyromonas, etc.
Anaerobic Gram-Negative bacteria examples
- Bacteroides fragilis: A major cause of intra-abdominal infections.
- Fusobacterium spp.: Associated with Lemierre’s syndrome and periodontal diseases.
- Prevotella spp.: Common in dental and respiratory infections.