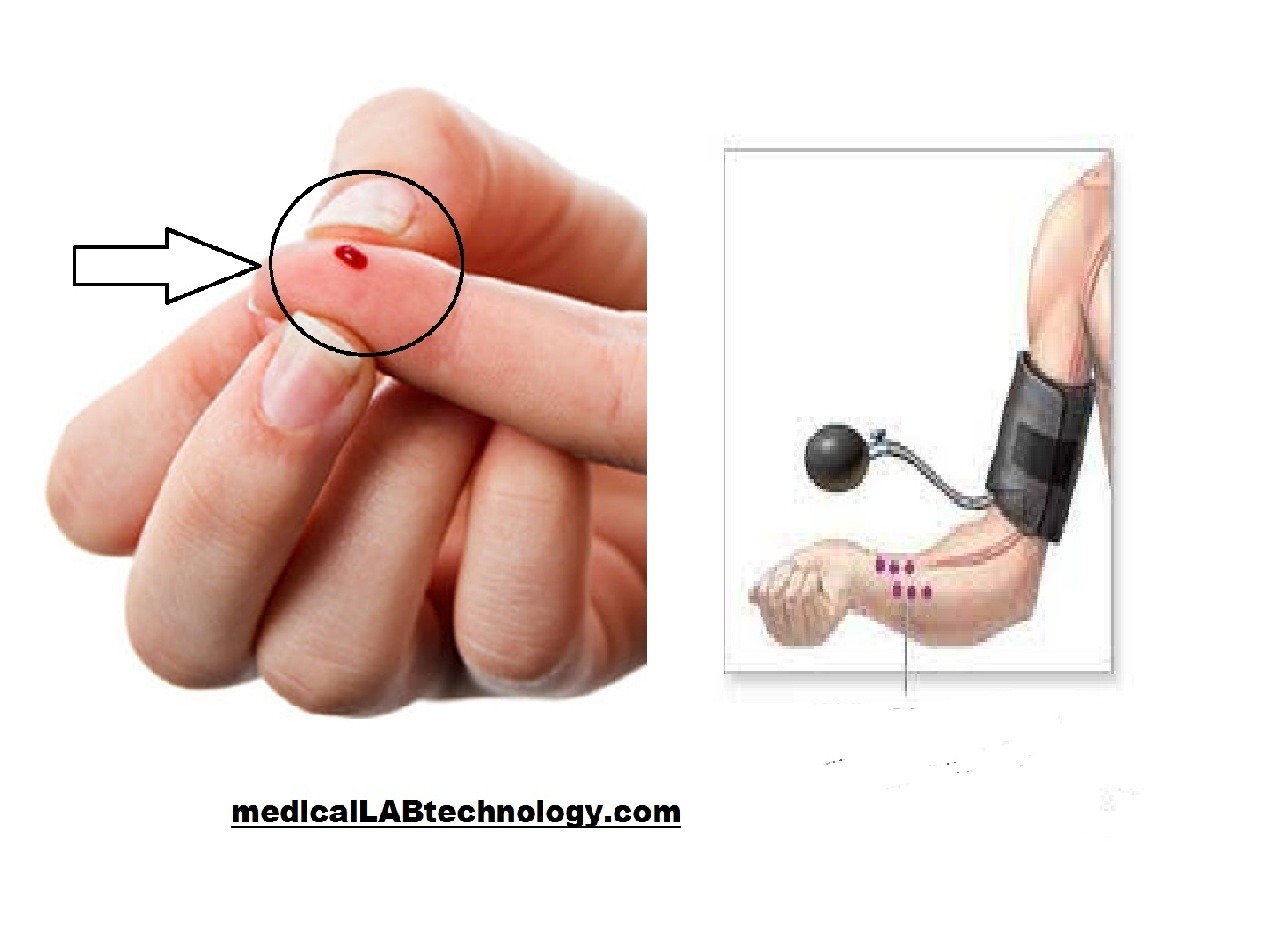
Bleeding time or BT is used to assess the ability of blood to clot by measuring the time it takes for bleeding to stop after a standardized skin puncture. It provides information about platelet function and the initial phase of hemostasis.
During bleeding, platelets adhere to the damaged blood vessels, aggregate together, and form a plug to stop the bleeding. The duration of bleeding time reflects the effectiveness of this process.
Here’s the video of Principle of bleeding time , Dukes and Ivy’s methods procedure significance.
By measuring bleeding time, healthcare professionals can evaluate platelet function and identify potential bleeding disorders or abnormalities in hemostasis.
What are the Bleeding time test requirements?
- Lancet
- Filter paper
- Sphygmomanometer
- Stopwatch
There are two methods for measuring the bleeding time (BT).
- Duke’s Method: Sometimes this method is used to check the infant BT.
- Ivy’s Method: It is the standard method for estimating the bleeding time.
Bleeding time duke method procedure
The principle of bleeding time duke method is that an incision is made on the ear lobe, the pupil of a finger, or the heel. These sites are rich in capillaries. Time note until blood stop. Following are the steps in dukes method.
- 1st clean the site of the incision with a spirit swab.
- Allow drying.
- Puncture deeply, so that blood flows out freely. Start the stopwatch. Blot the cut area with filter paper.
- Keep on going until blood stop flowing there. At this time stop the stopwatch and note the time. This is bleeding time.
Ivy method bleeding time procedure
Ivy method is standard for bleeding time estimation. Following are the steps.
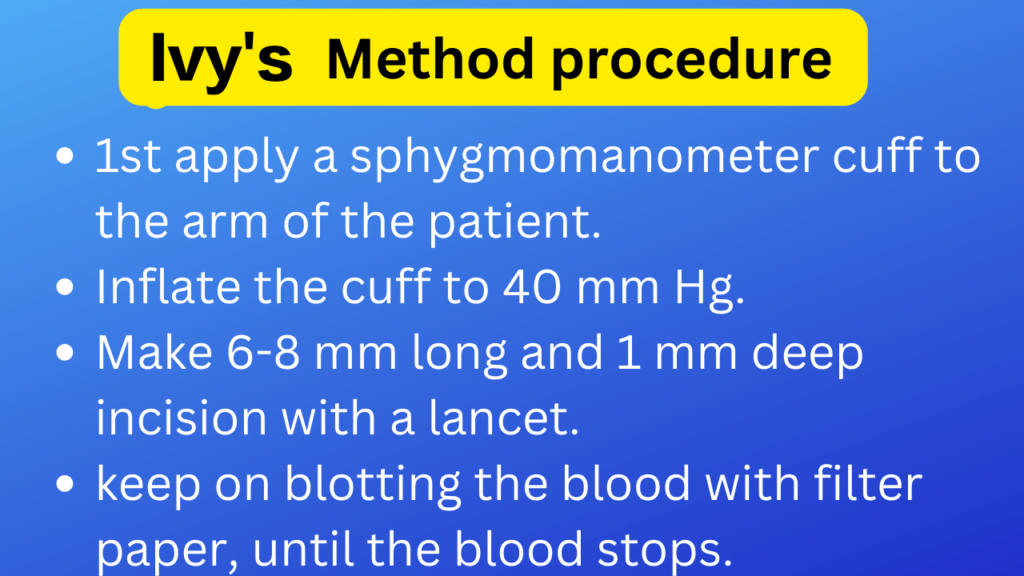
- 1st apply a sphygmomanometer cuff to the arm of the patient.
- Inflate the cuff to 40 mm Hg. This pressure should be maintained throughout the test.
- Clean the forearm with a spirit swab.
- Make 6-8 mm long and 1 mm deep incision with a lancet.
- keep on blotting the blood with filter paper, until the blood stops.
- Stop the stopwatch and note the time.
If the bleeding time is more than 15 minutes, and blood is still oozing. stope the test and apply pressure until the blood stops. Write the result, Bleeding time more than 15 minutes..
What is the BT(Bleeding time) test normal range(Reference Range)
- Dukes method: 3 to 7 mint
- Ivey’s method (lancet): 2 to 7 mints
- Ivey’s method (Template): 3 to 9 mints
Factors affecting bleeding time
Following are the factors which affect the bleeding time
- Number of platelets
- Function of platelets
- Willebrand disease. In this disease, platelets lack Von Willebrand Factor.
List of 5 diseases, which increase the bleeding time.
- Thrombocytopenia
- Von Willebrand disease
- Platelet function defect
- Afibrinogenaemia
- Aspirin Ingestion
Clinical significance of bleeding time
A bleeding time test (BT test) is important before any kind of surgery. When the patient’s BT test results are within normal range, the doctor performs an operation without any kind of hesitation. But if the BT test range is more than 15 minutes then special precautions are taken before surgery, so that blood can stop in the cut area.
what are the 3 main Sources of error in bleeding time calculation
- The superficial cut results in a bleeding time error.
- Blood pressure and variations in incision size result in bleeding time errors. Therefore standard incisions should be made.
- The incision area should be clear of visible veins.
What causes decreased bleeding time?
Bleeding time (BT) directly links to platelets because these platelets are used to make clots on the cut site. Therefore Bleeding time directly links to the platelet amount in the blood.