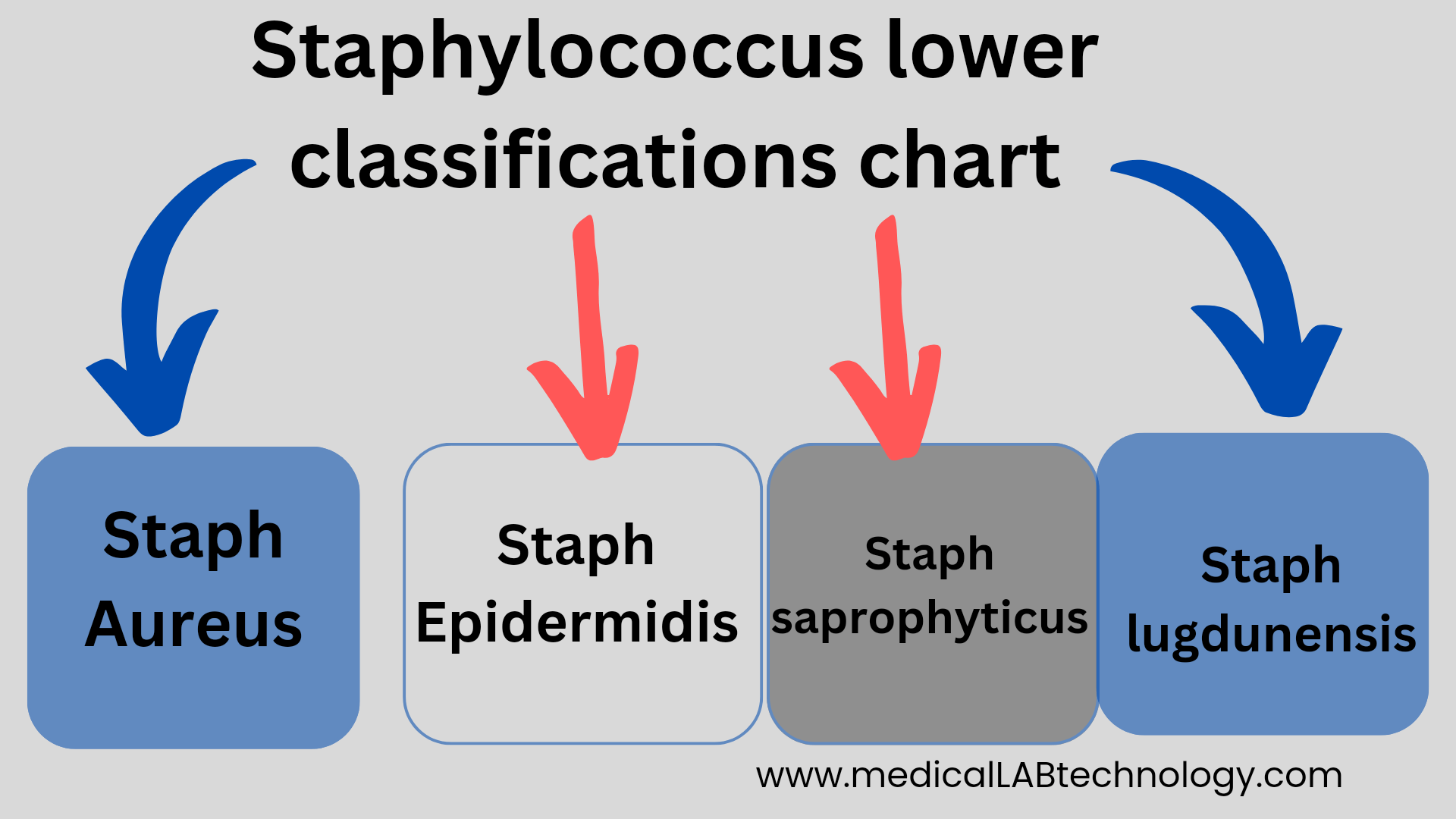
Staphylococcus lower classifications chart microbiology
Here’s the “Staphylococcus lower classifications “. Staphylococcus is a genus of bacteria that includes several species which are classified on the base of gram staining, which are gram-positive, spherical-shaped bacteria that are commonly found on the skin and mucous membranes of humans and animals. These bacteria are known for their ability to cause a variety … Read more