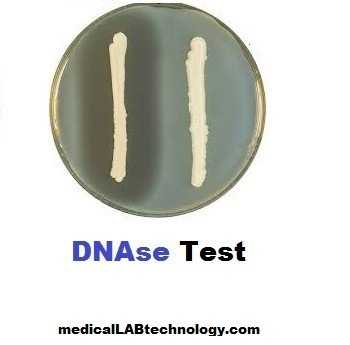
The deoxyribonuclease test (DNAse) is an important biochemical test for the conformation of staph aureus.
Principle of Deoxyribonuclease test (DNAse)
Staph aureus has an enzyme called DEOXYRIBONULEASE. When DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) reacts with staph aureus, its enzyme( DEOXYRIBONULEASE ) hydrolyzes the DNA.
Which reagents are used for the DANse test?
Basically, two reagents are used for the DNAse tests.
- 1. culture media containing deoxyribonucleic acid.
- 2. 3.6% Hydrochloric acid (Hcl)
Deoxyribonuclease test (DNAse) procedure
- Divide the culture media plate (containing Deoxyribose nucleic acid) into the required number by marking it under the culture plate.
- Using sterile loop, pick the colony and inoculate the test organism.
- Inoculate the positive and negative control on the same plate.
- Incubate that plate overnight at 37 C.
- In the morning, cover the plate with hydrochloric acid.
- Look for clearing around the colony after 5 minutes ( after adding Hydrochloric acid).
Which bacteria are Deoxyribonuclease test (DNAse) positive?
Only Staph aureus bacteria have DNAse enzymes. Therefore it is Deoxyribonuclease test (DNAse) positive bacteria.
which bacteria are Deoxyribonuclease test (DNAse) negative?
Bacteria other than staph aureus are Deoxyribonuclease test (DNAse) negative, due to lack of DEOXYRIBONULEASE enzyme.
what is the importance of Deoxyribonuclease test (DNAse)?
The Deoxyribonuclease test (DNAse) is an important test for the distinguish staph aureus and other strains of staph like the epidermidis.