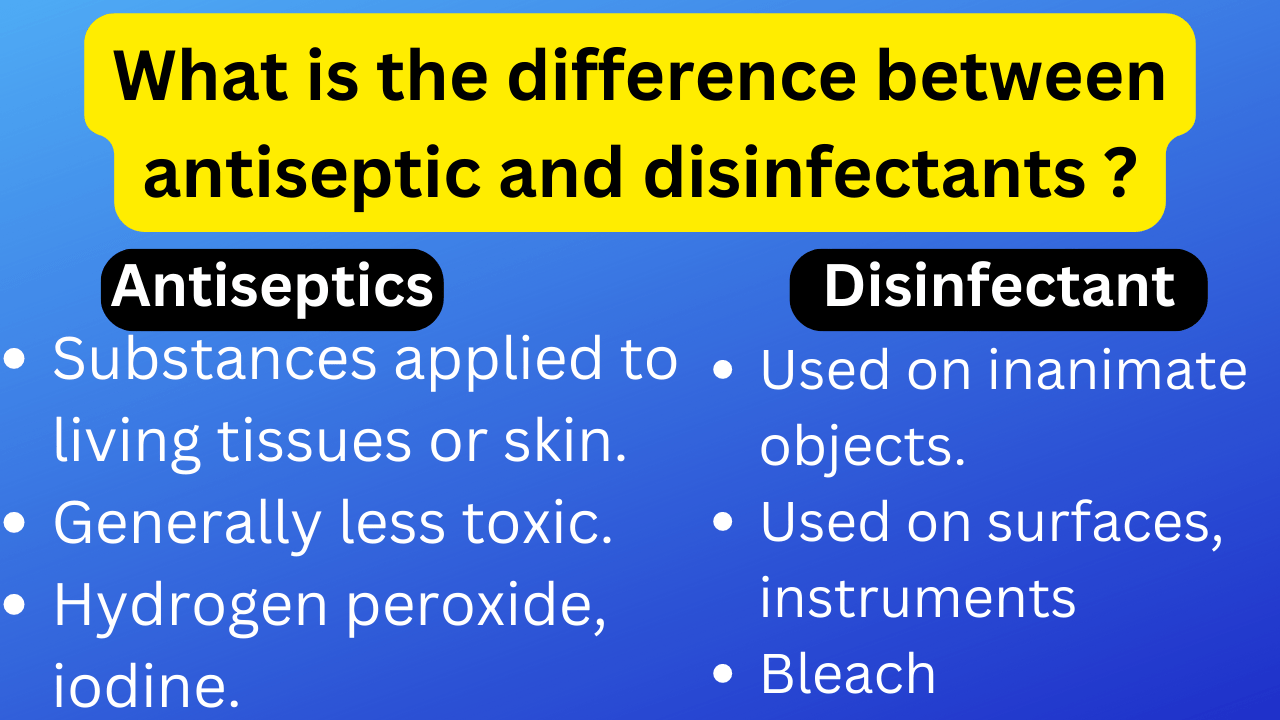
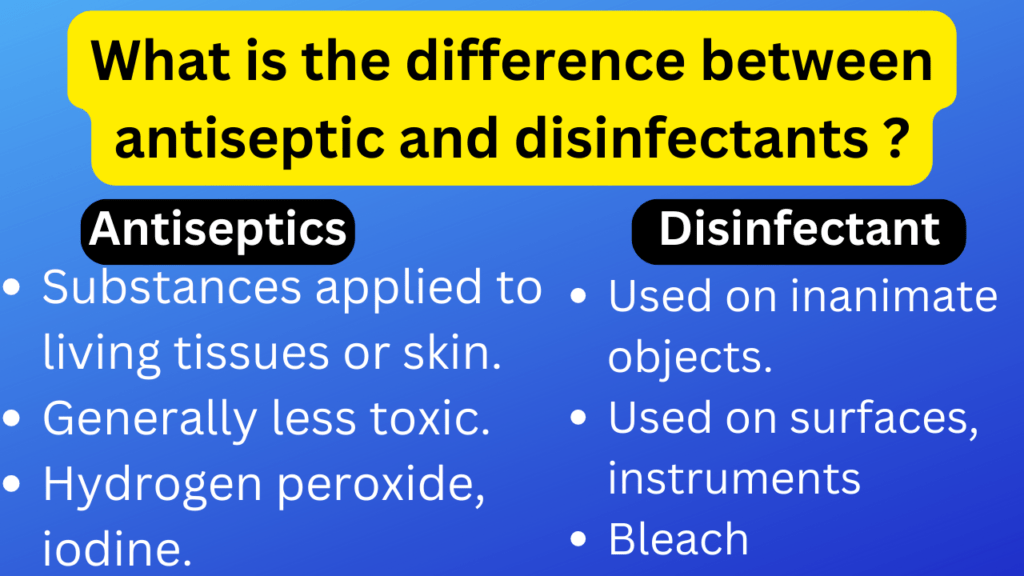
Here’s the difference between antiseptic and disinfectants in table from.
| Antiseptics | Disinfectant | |
| Definition | Substances applied to living tissues or skin | Substances used on inanimate objects or surfaces |
| Purpose | Prevent or inhibit the growth of microorganisms | Kill or eliminate microorganisms |
| Application | Used on skin, mucous membranes, or external body parts | Used on surfaces, instruments, equipment, and objects |
| Target | Used to prevent infection in living tissues or wounds | Used to eliminate or reduce microbial contamination |
| Concentration | Generally lower concentration for safety on tissues | Higher concentration to ensure effective disinfection |
| Toxicity | Generally less toxic and safer for use on living tissues | May be more toxic and not suitable for direct skin contact |
| Duration of Action | Shorter duration of action, require frequent application | Longer-lasting action, may not require frequent reapplication |
| Example | Hydrogen peroxide, iodine, alcohol, chlorhexidine | Bleach, quaternary ammonium compounds, phenols |
Disinfectants are chemicals to kill the vegetative form of bacteria, viruses, and fungi. It eliminates microorganisms by distracting their lipid, protein, and nucleic acid.
NOTE: Disinfectant does not eliminate spores and non-vegetative forms of the microorganisms, cleaning the NON-LIVING surface or OBJECTS have been in contact with body fluid or pathological tissue in the clinical laboratory.
Classification of antiseptic and disinfectant in microbiology
In microbiology, antiseptic and disinfectant are classified into two groups.
- Disinfectant
- Antiseptic
WHAT is Disinfectant in Microbiology?
Disinfectants are chemicals. They are applied to non-living things. These chemicals are toxic and corrosive to living tissue.
What are the 7 different Types of Disinfectants in the clinical laboratory?
There are eight types of disinfectants we use. Each type has a different composition.
- Phenolic Compound. Phenol is used for cleaning the floor, washroom, and bedpans. Examples Phenol, Dettol.
- Metallic Salts: Mercuric Chloride is used as a skin disinfectant. Nitrate 1 % is used for gonococcal eye infections.
- Formaldehyde: It is a rapid bacteriocidal disinfectant. 10 % solution used as a fixative in histopathology lab.
- Halogen: Chlorine used for disinfecting food and water. Tincture and iodine are used as skin disinfectants.
- Soap and Detergents: There are multipurpose disinfectants.
- Volatile: Ethyl alcohol in 70% solution used as skin disinfectant before injection.
- Gaseous Compounds: Ethylene oxide can use as a disinfectant.
What is an Antiseptic and what examples?
Antiseptic is a nontoxic substance for living surfaces like wounds or cuts on the body. Antiseptics are effective for cleaning wounds. Examples Alcohol, spirit, iodine
NOTE: It is the same chemicals as disinfectants. these chemicals are in reduced concentration on the skin.
What is an Antiseptic and what examples?
Examples: Alcohol, spirit, iodine