Here you will understand the main difference between endotoxin and exotoxin in microbiology.
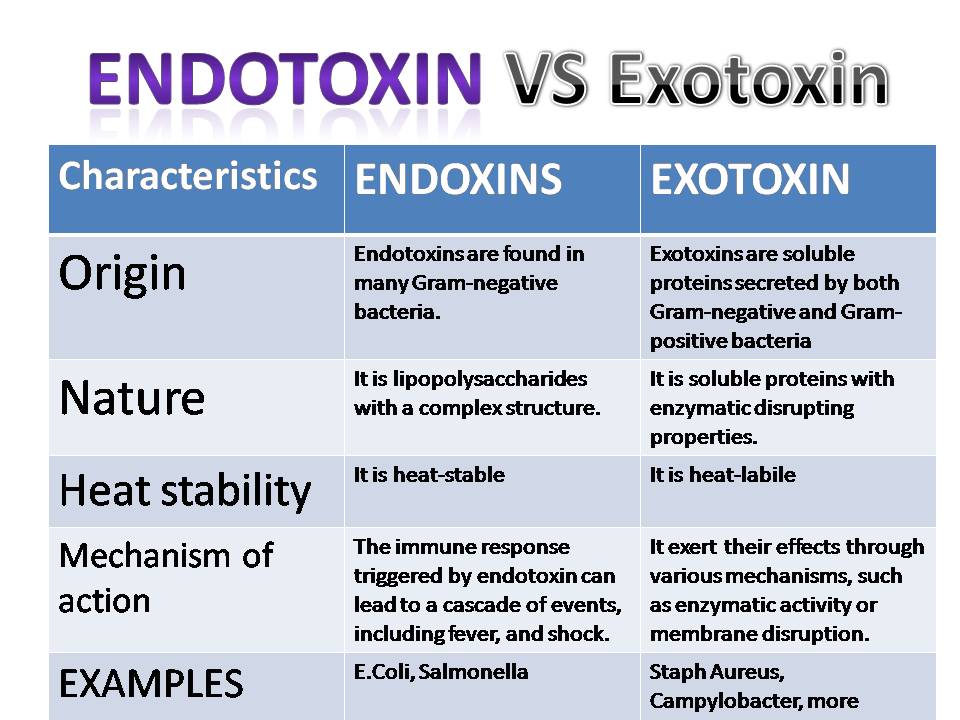
Endotoxin and exotoxin are produced by various bacteria. Both play critical roles in bacterial pathogenesis. There are many differences between endotoxins and exotoxins on the base structure, mechanisms of action, and their impact on human health.
What is Endotoxin in microbiology
Endotoxins are components of the cell wall of Gram-negative bacteria. It is primarily lipopolysaccharides (LPS). LPS are an integral part of the bacterial structure and are released when the bacterial cell dies or undergoes lysis.
Endotoxins are found in many Gram-negative bacteria. Examples are Escherichia coli, Salmonella spp, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Structure
- Endotoxins are composed of three parts: lipid A, core polysaccharide, and O antigen.
- Lipid A is the toxic moiety responsible for the harmful effects of endotoxins.
Mechanism of Action of endotoxin
- It primarily activates the host’s immune system, leading to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-1 (IL-1) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha).
- The immune response triggered by endotoxins can lead to a cascade of events, including fever, and shock.
Clinical Effects of endotoxin
- It is implicated in sepsis, a life-threatening condition characterized by a systemic inflammatory response to infection.
- Septic shock, marked by a severe drop in blood pressure, is a critical consequence of endotoxin exposure.
What is Exotoxin in microbiology
Exotoxins are soluble proteins secreted by both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. It targets specific host cells and interferes with their normal functioning, often causing severe damage.
Structure
- Exotoxins are typically composed of one or more protein subunits.
- They are heat-labile and can be denatured by moderate heat.
Mechanism of action of exotoxin
- It exert their effects through various mechanisms, such as enzymatic activity or membrane disruption.
- Some exotoxins inhibit protein synthesis within host cells, while others disrupt cell membranes or interfere with signal transduction pathways.
Clinical Effects of Exotoxins
- Exotoxins are responsible for a wide range of bacterial diseases, including diphtheria (Corynebacterium diphtheriae exotoxin), botulism (Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin), and tetanus (Clostridium tetani neurotoxin).
- These toxins can cause paralysis, muscle spasms, and even death if left untreated.
3 main differences between endotoxin and exotoxin in microbiology
Origin
- Endotoxins are part of the bacterial cell wall and are released when the cell is disrupted.
- Exotoxins are secreted by bacteria into the extracellular environment.
Nature
- Endotoxins are lipopolysaccharides with a complex structure.
- Exotoxins are soluble proteins with enzymatic or membrane-disrupting properties.
Heat stability
- Endotoxins are heat-stable.
- Exotoxins are heat-labile and can be destroyed by moderate heat.
1 thought on “Difference between endotoxin and exotoxin in microbiology”