Here you will learn about “what is ELISA test principle procedure types”
ELISA or Enzyme-linked immunosorbent Assay is a widely used biochemical technique that plays a crucial role in the detection and quantification of proteins, peptides, antibodies, and hormones.
What is the principle of ELISA test
It involves immobilizing the antigen of interest onto a solid surface, such as a microtiter plate. Subsequently, an enzyme-linked antibody is added, forming a complex with the antigen.
Procedure of ELISA test step by step
- Coating
The first step involves coating a solid surface (typically a microtiter plate) with the antigen of interest. This can be achieved by directly adsorbing the antigen or by using a capture antibody that specifically binds to the antigen. - Blocking
To prevent non-specific binding, the coated surface is treated with a blocking agent, such as bovine serum albumin (BSA) or non-fat milk. This ensures that only the target antigen or antibody interacts with the surface. - Incubation with Sample
The test sample, which may contain the antigen or antibody of interest, is added to the coated and blocked wells.- NOTE: If the target substance is present, it will bind to the immobilized molecule on the surface.
- Washing
Unbound substances are removed by washing the plate, ensuring that only specific interactions are retained. - Enzyme-Linked Antibody Addition
An enzyme-linked antibody, specific to the target antigen or antibody, is added. This forms a complex with the bound antigen. - Second Washing
Excess enzyme-linked antibodies are removed by washing the plate again. - Substrate Addition
A substrate for the enzyme is added, and the enzyme catalyzes a reaction that produces a detectable signal.- Most commonly used substrates include chromogenic substances that result in a color change.
- Signal Measurement
The intensity of the developed color is measured spectrophotometrically, and the concentration of the target substance is determined by comparing it to a standard curve.
Types of ELISA (Direct, Indirect, Sandwich, Competitive)
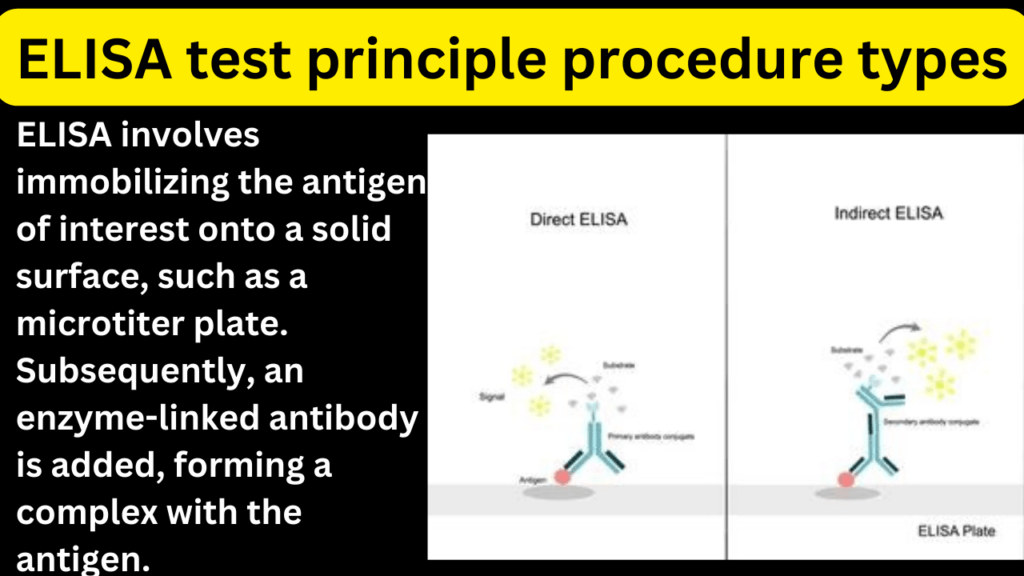
Direct ELISA
In this type, the antigen is directly immobilized on the solid surface. The enzyme-linked antibody is then added to detect the bound antigen.
Indirect ELISA
In this type, the antigen (Ig) is immobilized, and an unlabeled primary antibody is added. A secondary enzyme-linked antibody, specific to the primary antibody, is then introduced.
Sandwich ELISA
This type utilizes two antibodies – one to capture the antigen and another enzyme-linked antibody to detect it. It is highly sensitive and commonly used for quantifying antigens.
Competitive ELISA
In competitive ELISA, a known amount of enzyme-labeled antigen competes with the sample antigen for binding to a limited amount of immobilized antibody.