Crossing over is a crucial process that occurs during meiosis, the cell division responsible for the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells) in sexually reproducing organisms. This process plays a significant role in generating genetic variation among offspring.
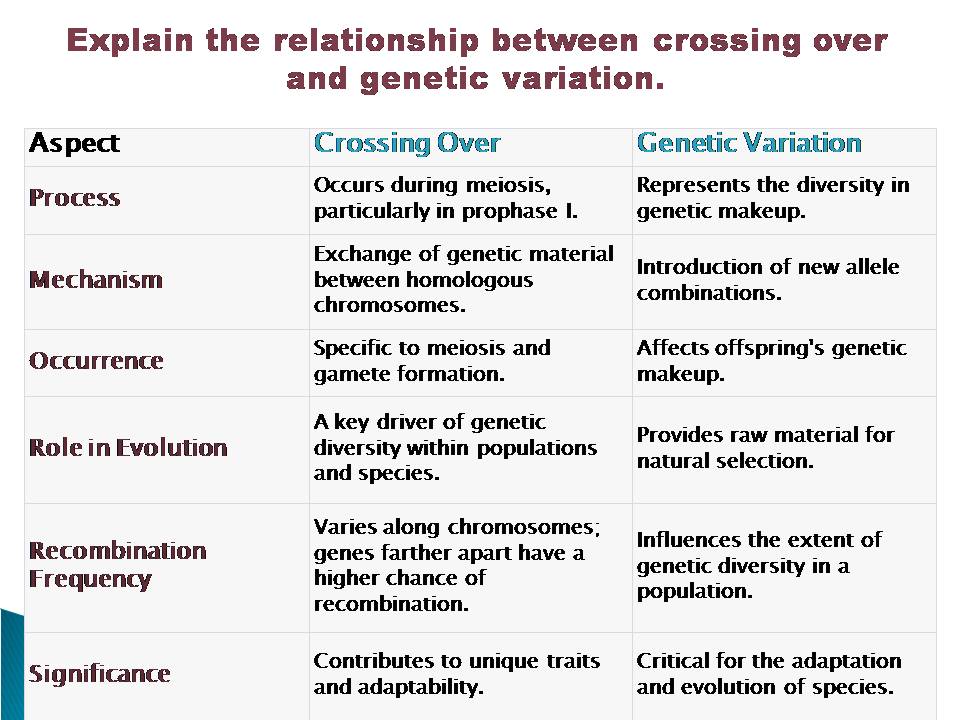
Here’s an explanation of the relationship between crossing over and genetic variation.
1. Introduction to Crossing Over:
- Crossing over, also known as genetic recombination, is an event that happens during the prophase I stage of meiosis.
- During prophase I, homologous chromosomes (chromosomes with the same genes but potentially different alleles) come together and align.
- At this point, small sections of chromatids from one homologous chromosome can break and exchange places with the corresponding sections of chromatids from the other homologous chromosome.
- As a result, genetic material is swapped between homologous chromosomes, leading to a mix of genetic information.
2. Creating New Combinations:
- Crossing over creates novel combinations of alleles on chromosomes. Since each homologous chromosome carries different alleles, the exchange of genetic material between them results in new combinations of alleles on the chromatids.
- These new allele combinations can lead to unique genetic traits and characteristics in the offspring.
3. Genetic Diversity:
- Genetic diversity refers to the variety of different genetic characteristics within a population or species.
- Crossing over is a primary mechanism contributing to genetic diversity. By shuffling alleles between homologous chromosomes, it introduces variability in the genetic makeup of gametes.
- When these gametes fuse during fertilization to form a zygote, the resulting individual inherits a combination of genetic material from both parents, including the allele combinations generated by crossing over. This combination is unique, contributing to the genetic diversity of the population.
4. Recombination Frequency:
- The frequency of crossing-over events can vary along the length of chromosomes. Some regions may undergo crossing over more frequently than others.
- The farther apart two genes are on a chromosome, the more likely they are to experience a crossing-over event between them.
- Geneticists use recombination frequencies to map the relative positions of genes on chromosomes, a technique known as genetic mapping.
5. Role in Evolution:
- Genetic variation generated by crossing over is a fundamental driver of evolution. It provides the raw material upon which natural selection can act.
- New combinations of alleles may result in traits that are advantageous in certain environments, allowing individuals with these traits to have a better chance of survival and reproduction.
- Over generations, this process can lead to the gradual accumulation of beneficial traits within a population, contributing to the evolutionary process.
NOTE: Crossing over during meiosis is a process of genetic recombination that promotes genetic diversity by shuffling alleles between homologous chromosomes.