Here you will learn about fume hood vs biosafety cabinet.
In laboratories and research facilities, safety and containment are paramount concerns. Two essential tools used to ensure the safety of researchers and the integrity of experiments are fume hoods and biosafety cabinets.
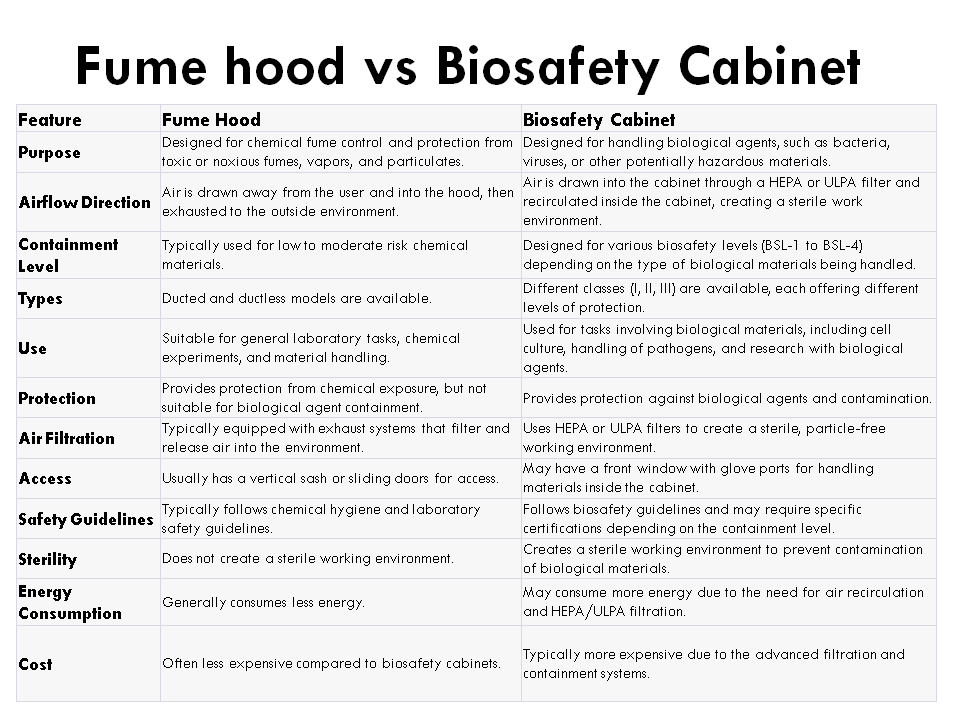
While both serve crucial roles in maintaining a controlled environment, they are designed for different purposes and offer distinct features.
In this article, we’ll explore the fume hood vs biosafety cabinet and when and why each is used.
What is Fume Hood
A fume hood is also known as a chemical hood or exhaust hood. It’s used for the removal of hazardous fumes, vapors, and particulate matter.
It provides a barrier between the laboratory worker and potentially harmful chemicals and allows for the safe ventilation of these substances.
Here are some important features of fume hoods:
- Ventilation and Airflow: Fume hoods are designed to capture and exhaust chemical fumes away from the researcher. They have an inward airflow that prevents contaminants from escaping into the laboratory.
- Protection: Fume hoods protect researchers from chemical exposure and inhalation of harmful substances, making them essential for handling volatile or noxious chemicals.
- Open Front Design: Fume hoods typically have an open front, allowing researchers to perform tasks inside while maintaining a physical barrier between themselves and the chemicals.
- Usage: Fume hoods are commonly used in chemistry laboratories and industries where the primary concern is the containment and removal of chemical vapors.
- Classifications: Fume hoods can be classified into ducted and ductless types, each with specific applications and maintenance requirements.
What is a Biosafety Cabinet
A biosafety cabinet (BSC) is a device designed to provide both a sterile environment for research involving biological materials and protection for the operator.
Unlike fume hoods, biosafety cabinets are specifically engineered for the safe handling of biological agents, including pathogens and microorganisms.
Here are some key characteristics of biosafety cabinets:
- Sterile Environment: BSCs maintain a sterile environment by using HEPA filters to filter incoming and outgoing air, preventing the escape of biological agents and protecting the researcher from contamination.
- Safety Levels: Biosafety cabinets are classified into three levels (BSL-1, BSL-2, and BSL-3) based on the level of containment and the types of biological agents they can handle.
- Front Window: BSCs have a transparent front window made of safety glass or plastic that allows researchers to work inside the cabinet. This window acts as a physical barrier, similar to a fume hood.
- Usage: Biosafety cabinets are commonly used in research labs, clinical laboratories, and healthcare facilities for work involving infectious agents, cell cultures, and other biohazardous materials.
- Personnel and Environmental Protection: In addition to protecting the materials being handled, BSCs also protect laboratory personnel and the surrounding environment from exposure to potentially dangerous biological agents.