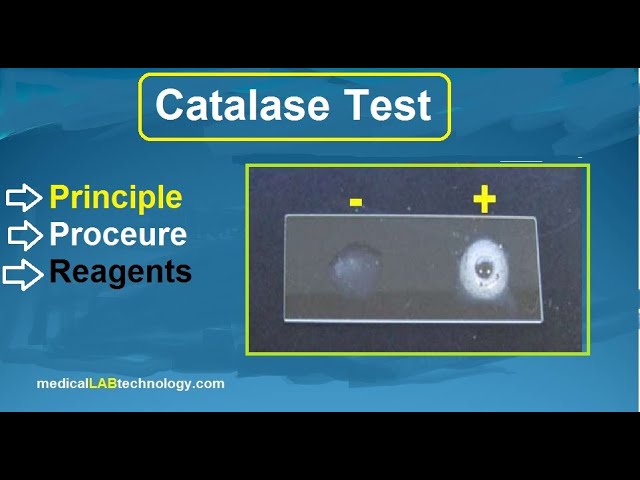
Catalase test is important for identification of varius bacteria specially staphylococcus aureus in microbiology.
Here we learn about principle of catalase test, procedure and the reagents.
Catalase test principle microbiology
Catalase synthesized by some bacteria acts as a catalyst in the breakdown of Hydrogen peroxide (3% H2O2) results in the production of Oxygen gas (O2) and water (H2O).
Catalase test Procedure microbiology
- First of all, add 2 to 3 ml hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) solution in the test tube.
- In the next step, take the bacteria colony from culture media with a glass rod or wooden rod. Mix this colony in the test tube having hydrogen peroxide solution.
- Look into the solution for bubbling. It shows the synthesis of oxygen (O2).
Catalase test reagent microbiology
3% Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) use as catalase reagent.
Catalase positive bacteria list microbiology
Staphylococcus species produced oxygen, and they are called as catalase positive bacteria. Here is the list of catalase positive bacteria.
| 1 | Staph Aureus |
| 2 | Staph Epidermidis |
| 3 | Staph Saprophyticus |
Catalase negative bacteria list microbiology
Streptococcus species bacteria don’t produce oxygen while reacting with hydrogen peroxide. Therefore they are called catalase-negative bacteria.
| 1 | Streptococcus Pyogenes |
| 2 | Streptococcus agalactiae |
| 3 | Streptococcus Pneumonia |
| 4 | Enterococcus |
Quality control for catalase test microbiology
Always run known positive and negative control with test batch.
Here’s the video of “catalase test principle procedure in microbiology”.