Here you will learn about “what is Spread plate technique in microbiology”.
In the field of microbiology, accurate and reliable quantification of microorganisms is of utmost importance. Researchers and scientists often rely on various techniques to estimate the number of viable cells in a given sample.
Here’s the video of Spread plate technique principle procedure steps in microbiology.
One such indispensable method is the spread plate technique, mostly used in laboratories around the world. The spread plate technique offers a simple yet effective way to enumerate microbial populations and assess their growth characteristics.
Spread plate technique principle
The spread plate technique in microbiology involves diluting a sample, spreading it on a solid agar medium, and incubating it. Individual colonies that form on the agar plate represent viable microorganisms present in the original sample.
It allows for quantification and isolation of microorganisms, providing valuable information for microbial analysis.
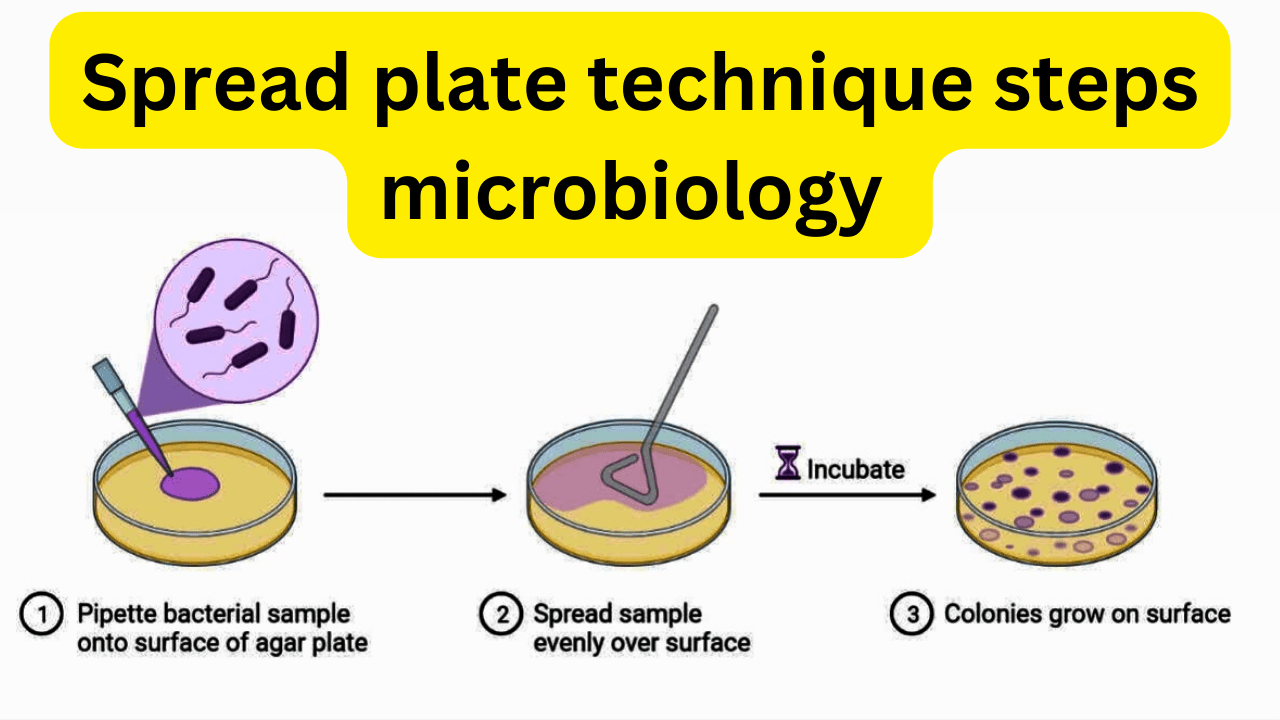
Spread plate method procedure microbiology
The spread plate technique in microbiology follows a series of procedure steps to obtain individual bacterial colonies on a solid agar medium. Here are the key steps involved in the spread plate technique:
- Dilution
- Agar plate Preparation
- Spreading
- Incubation
- Colony Observation
- Colony Counting
- Data Analysis
- Dilution: Take a known volume of the original sample and perform serial dilutions to obtain a range of dilutions. This helps to reduce the number of microorganisms in the sample and ensure a countable range of colonies.
- Agar plate Preparation: Prepare solid agar plates containing appropriate nutrients and selective agents or indicators, depending on the purpose of the analysis.
- Spreading: Using a sterile spreader or a glass rod, transfer a small volume (usually 0.1 mL or 0.01 mL) of the diluted sample onto the surface of the solid agar plate.
- Incubation: Place the agar plates in an incubator set at the appropriate temperature and conditions suitable for the growth of the microorganisms under investigation.
- After the incubation period, examine the agar plates for the presence of visible colonies. Record the characteristics of the colonies, such as size, shape, color, and any other relevant observations.
- Count the individual colonies on the agar plate, taking care to avoid counting overlapping. Depending on the desired accuracy, count colonies on plates with an appropriate number of colonies (usually between 30 and 300).
- Analyze the results obtained from the colony count to determine the concentration or abundance of viable microorganisms in the original sample.
- Note: Calculate and express the results as CFUs per unit volume or per gram of the original sample
Note: Multiply the colony count by the appropriate dilution factor to calculate the number of CFUs in the original sample.

Differentiate between spread plate technique and streak plate technique with suitable diagram