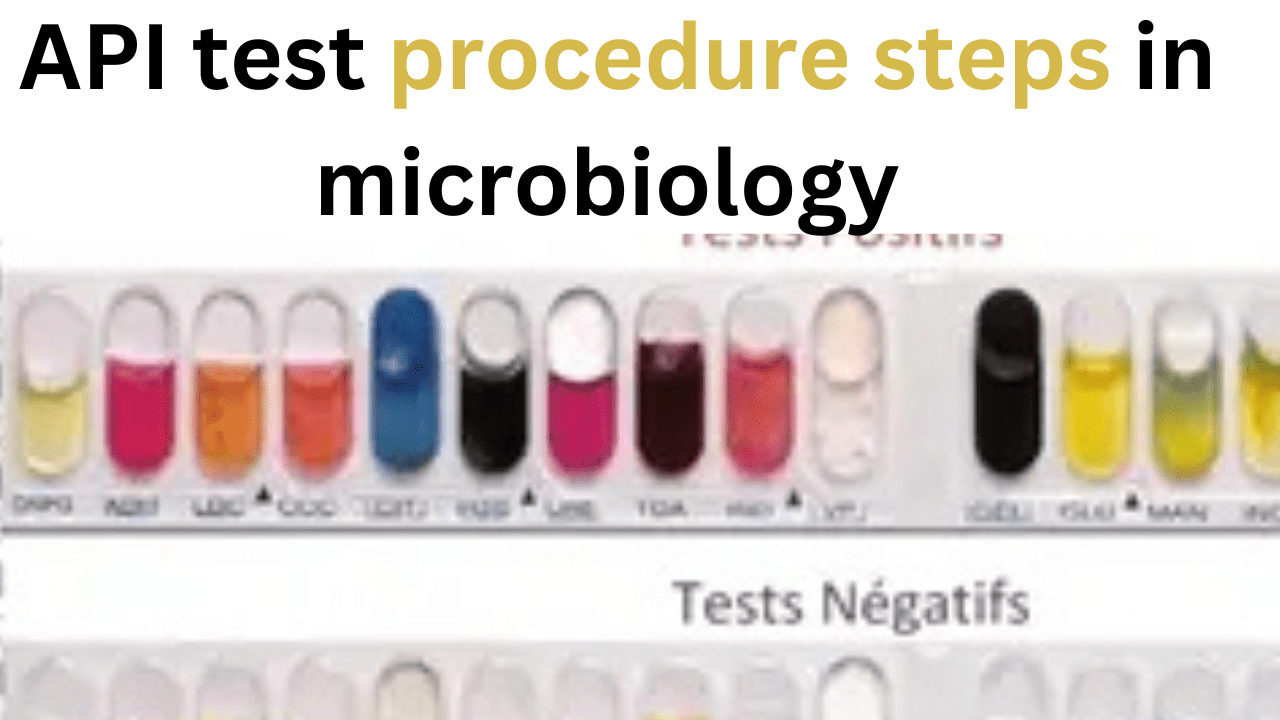
The API test (Analytical Profile Index) in microbiology , is a biochemical panel-based testing system used to identify microorganisms, primarily bacteria and yeast, by determining their metabolic and enzymatic activities.
API Test Microbiology Procedure steps
Materials Required
- API test strip (e.g., API 20E, API 20NE).
- Distilled water.
- Sterile inoculating loops.
- Sterile test tubes.
- Incubator set to the appropriate temperature.
- Microbial culture (pure isolate).
- API database.
Analytical Profile Index test procedure
- Obtain a pure culture of the microorganism to be tested.Prepare a suspension of the organism in distilled water to match the turbidity equivalent to a 0.5 McFarland standard.
- Open the API strip and place it on a clean, sterile surface.Fill the API strip’s wells with sterile distilled water to create a humid environment.
- Using a sterile pipette or loop, inoculate each well of the API strip with the prepared microbial suspension.
- Place the inoculated strip in the incubation tray.Cover the tray with its lid and incubate at the recommended temperature and duration (e.g., 18-24 hours at 35-37°C).
- After incubation, observe and record the color changes or reactions in each well.
- Enter the results into the API database like manual codebook. Obtain the identification code and determine the organism based on the database.
Note: Always include positive and negative controls when running API tests to ensure accuracy.
Advantage and Disadvantage of Api test microbiology
Advantages
- Rapid identification compared to traditional methods.
- Simplified procedure with pre-made panels.
- Standardized conditions minimize variability.
- Extensive reference libraries enhance
Disadvantage
- Api works with isolated, pure cultures of microorganisms.
- Cannot always identify rare or atypical strains.
- Api May require additional tests for confirmation of results.