Gram-negative bacteria are a group of bacteria characterized by their thin peptidoglycan layer and an outer membrane containing lipopolysaccharides (LPS). They do not retain the crystal violet dye during the Gram staining process, appearing pink under a microscope.
Key Tests Explained
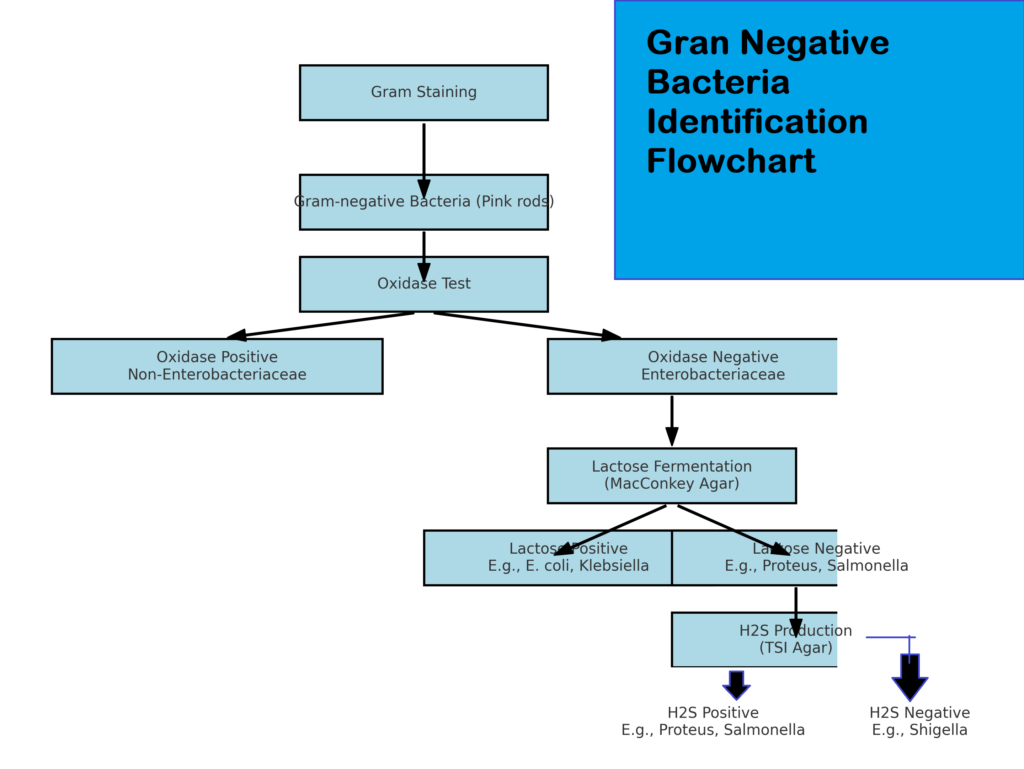
- You need to perform Gram Stain. It differentiates Gram-negative bacteria (pink) from Gram-positive bacteria (purple).
- Second Oxidase Test:
- Positive: Non-Enterobacteriaceae (Pseudomonas spp., Vibrio spp.).
- Negative: Enterobacteriaceae family.
- Triple Sugar Iron (TSI) Test:
- Fermentative: Acid slant and butt (yellow).
- Non-fermentative: Alkaline slant (red).
- Lactose Fermentation (MacConkey Agar):
- Positive: Pink colonies (E. coli, Klebsiella).
- Negative: Colorless colonies (Proteus, Salmonella).
- Hydrogen Sulfide (H₂S) Production:
- Positive: Black precipitate (Proteus, Salmonella).
- Negative: No blackening (Shigella).
- Urease Test:
- Positive: Pink color due to ammonia (Proteus).
- Negative: No color change (Salmonella).
Characteristics of gram negative bacteria
- Stain pink or red after decolorization and counterstaining with safranin in gram staining.
- Thin peptidoglycan layer.
- Outer membrane with LPS (endotoxin), which could trigger immune responses.
- Resistant to a few antibiotics because of the outer membrane.
- Often resistant to antibiotics like penicillin due to β-lactamase enzymes and efflux pumps.
- They cause many diseases like Urinary tract infections (E. coli).Gastroenteritis (Salmonella, Vibrio).Respiratory infections (Klebsiella, Pseudomonas).