The Quellung reaction, also known as the capsular swelling reaction, is a highly reliable technique. It is one of the classical microbiological techniques used to find Streptococcus pneumoniae.
This method is widely used in diagnostic laboratories. It confirms the presence of encapsulated pneumococci by the visible swelling of their polysaccharide capsule.
What Is the Quellung Reaction?
The Quellung reaction is an antigen–antibody reaction. In this reaction, the capsular polysaccharides antigen of bacteria reacts with specific antisera. This causes a visible enlargement of the capsule under a microscope. This phenomenon is particularly characteristic for S. pneumoniae, which possesses a prominent polysaccharide capsule.
Importance of the Quellung Reaction in Microbiology
- It helps confirm the identity of Streptococcus pneumoniae.
- Useful in differentiating encapsulated vs non-encapsulated strains.
- It Can help in serotyping pneumococci.
- Valuable in clinical diagnosis of pneumococcal pneumonia, meningitis, and septicemia.
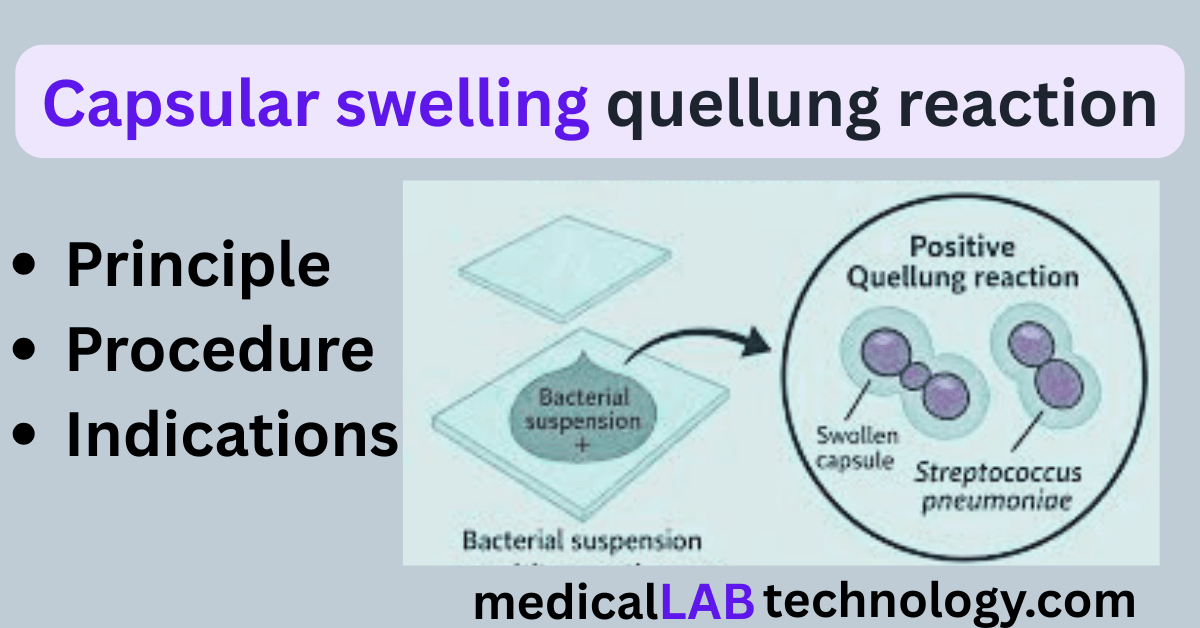
Principle of the Quellung Reaction
When bacteria possessing a capsule are mixed with type-specific antipneumococcal serum, the antibodies bind to the capsular antigens.
This antigen–antibody binding causes the bacterial capsule to appear swollen, enlarged, and more refractile under a microscope. The swelling does not mean the capsule grows; rather, it becomes more optically visible because of increased refractivity.
A contrasting dye helps visualize the capsule, making the reaction easier to interpret.
Procedure of the Quellung Reaction
Follow these standard laboratory steps to perform the test accurately.
Materials Required
- Fresh culture of Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Type-specific antipneumococcal antisera
- Methylene blue (or India ink)
- Clean microscope slide and cover slip
- Inoculating loop
- Light microscope (oil immersion)
1. Prepare the Bacterial Suspension
- Place a tiny colony of S. pneumoniae on a clean glass slide.
- Add 1 drop of sterile saline to make a smooth suspension.
2. Add the Specific Antiserum
- Add one drop of type-specific pneumococcal antiserum to the bacterial suspension.
- Mix gently.
3. Add Staining Dye
- Add a small drop of methylene blue or India ink to enhance visualization.
4. Apply Cover Slip
- Place a cover slip carefully to avoid air bubbles.
5. Examine Under Microscope
- Observe under oil immersion (1000x magnification).
Results and Interpretation
Positive Quellung Reaction
A positive reaction is indicated by:
- Capsule appears swollen, enlarged, and sharply outlined
- The bacterial cell looks more refractile and halo-like
- Clear demarcation between cell and background
This confirms the presence of encapsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Negative Quellung Reaction
A negative result shows:
- No swelling of the capsule
- Capsule appears faint or not visible
- Suggests either:
- Non-encapsulated S. pneumoniae, or
- Different organism without specific capsular antigens
Applications of the Quellung Test for Streptococcus pneumoniae in microbiology
Confirmatory identification in clinical labs
- Serotyping pneumococci based on capsular differences
- Useful in verifying vaccine-related serotypes
- Assists in epidemiological studies of pneumococcal infections
Conclusion
The Quellung reaction remains a gold-standard method for detecting the capsule of Streptococcus pneumoniae. This test utilizes antigen–antibody interactions to produce visible capsular swelling. It is simple yet effective.
It allows precise identification and serotyping of pneumococcal strains. Its reliability makes it an essential tool in clinical microbiology and infectious disease diagnostics.