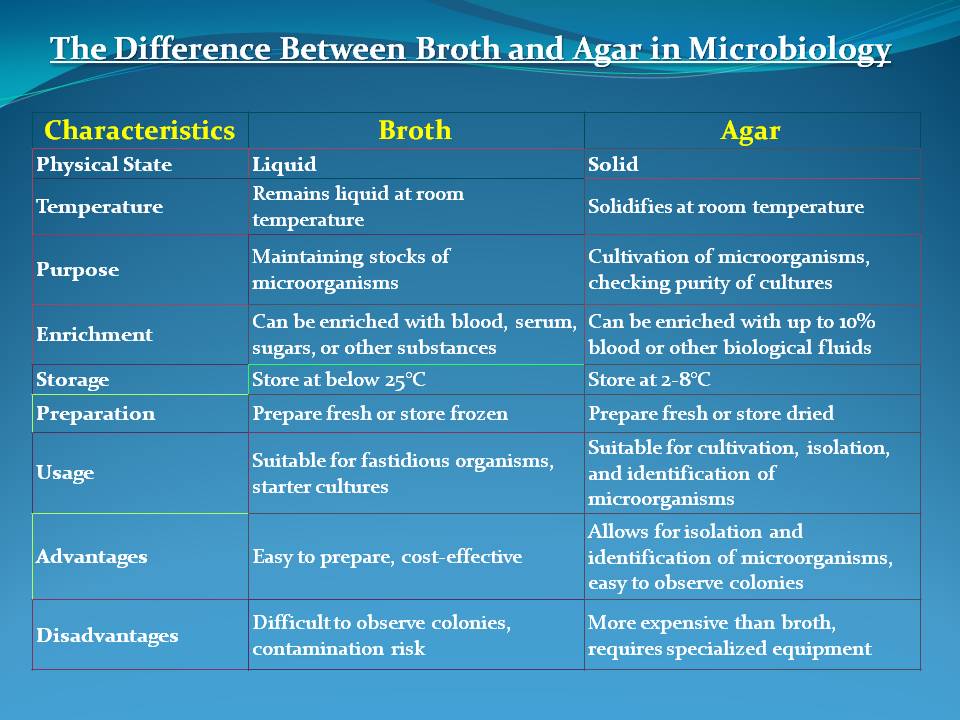
In microbiology, two common types of growth media are used to cultivate microorganisms: broth and agar. While they share similar compositions, the main difference between them lies in their physical state and purpose.
What is Broth media in microbiology?
A broth is a liquid medium used to maintain stocks of microorganisms. It is typically used to grow fastidious organisms and can be enriched with blood, serum, sugars, or other substances for special purposes.
Broth remains in a liquid form at room temperature and is often used as a starter culture for further experiments.
What is agar media in microbiology?
Agar is a solid growth medium that contains a solidifying agent, agar powder. This powder is derived from red algae and causes the medium to solidify at room temperature.
Agar is suitable for the cultivation of microorganisms and is often used to check the purity of cultures before performing biochemical or serological tests. It can be enriched with up to 10% blood or other biological fluids to meet specific experimental requirements.
2 Key Differences between broth media and agar media
- The main difference between broth and agar is their physical state. Broth remains in a liquid form, while agar solidifies at room temperature due to the presence of agar powder. This solidification makes agar suitable for the cultivation of microorganisms, whereas broth is better suited for maintaining stocks of microorganisms.
- Both broth and agar should be stored in a cool, dry place (10-30°C) and used before their expiration dates. Once prepared, broth should be stored at below 25°C, while agar should be stored at 2-8°C.