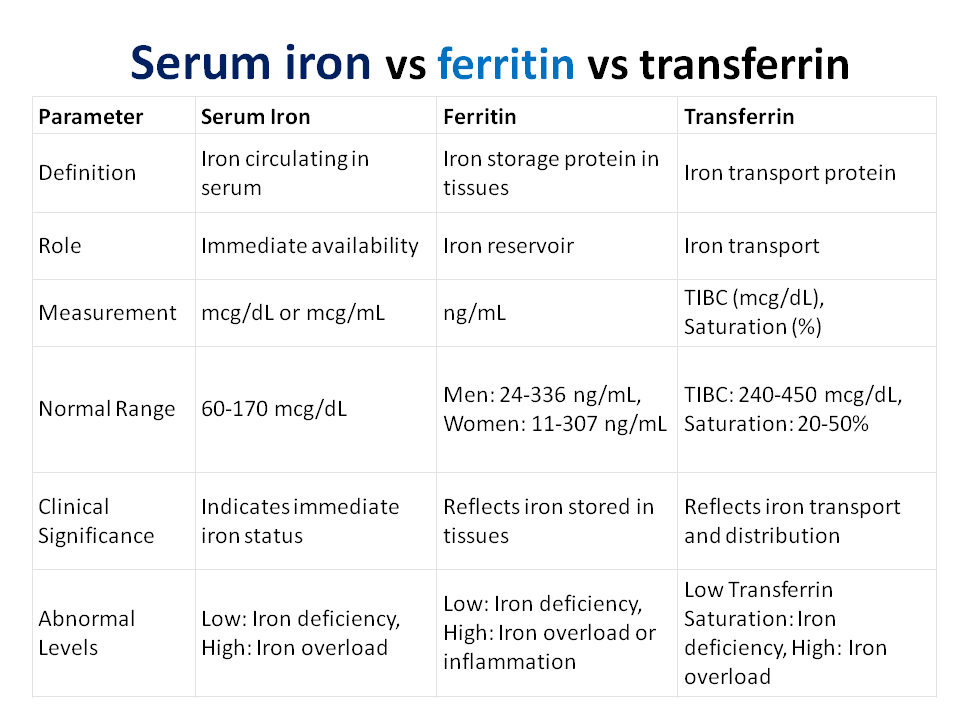
Transferrin is a protein that transports iron in the blood and delivers it to cells. While ferritin is a protein that stores iron, primarily in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow.
Serum Iron properties
- Serum iron measures the amount of iron circulating in the bloodstream that is bound to transferrin.
- It reflects the amount of iron that is immediately available for use by tissues and cells.
- Expressed in micrograms per deciliter (mcg/dL) or micrograms per milliliter (mcg/mL).
- Low levels may indicate iron deficiency, while high levels could suggest iron overload.
- S. Iron normal range: 60-170 micrograms per deciliter (mcg/dL)
Serum Ferritin properties
- It serves as a reservoir of iron and releases it into the bloodstream when needed.
- Expressed in nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL).
- Elevated levels may indicate inflammation, while low levels are associated with iron deficiency.
- Serum ferritin normal range.
- Women: 11-307 ng/mL
- Men: 24-336 nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL)
Transferrin properties
- It binds to iron and helps regulate its distribution in the body.
- Expressed as a percentage of saturation or total iron-binding capacity.
- Low transferrin saturation may suggest iron deficiency, while high levels can be seen in conditions like hemochromatosis.
- Normal range of transferrin:
- Total Iron-Binding Capacity (TIBC): 240-450 mcg/dL
- Transferrin Saturation: 20-50%