The Two-Step Tuberculosis (TB) Skin Test (also known as the Mantoux test) is a diagnostic method used to detect latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI). It is often required for healthcare workers, long-term care facility residents, and others at high risk of TB exposure.
The two-step process is performed to distinguish a boosted reaction from a new infection.
Why Two-Step Testing?
In some individuals, particularly those who have been exposed to TB in the distant past, the initial skin test may yield a false-negative result because their immune response has waned over time. The first test can stimulate (or “boost”) their immune system, and the second test then reveals the true result.
Procedure for Two-Step TB Skin Test
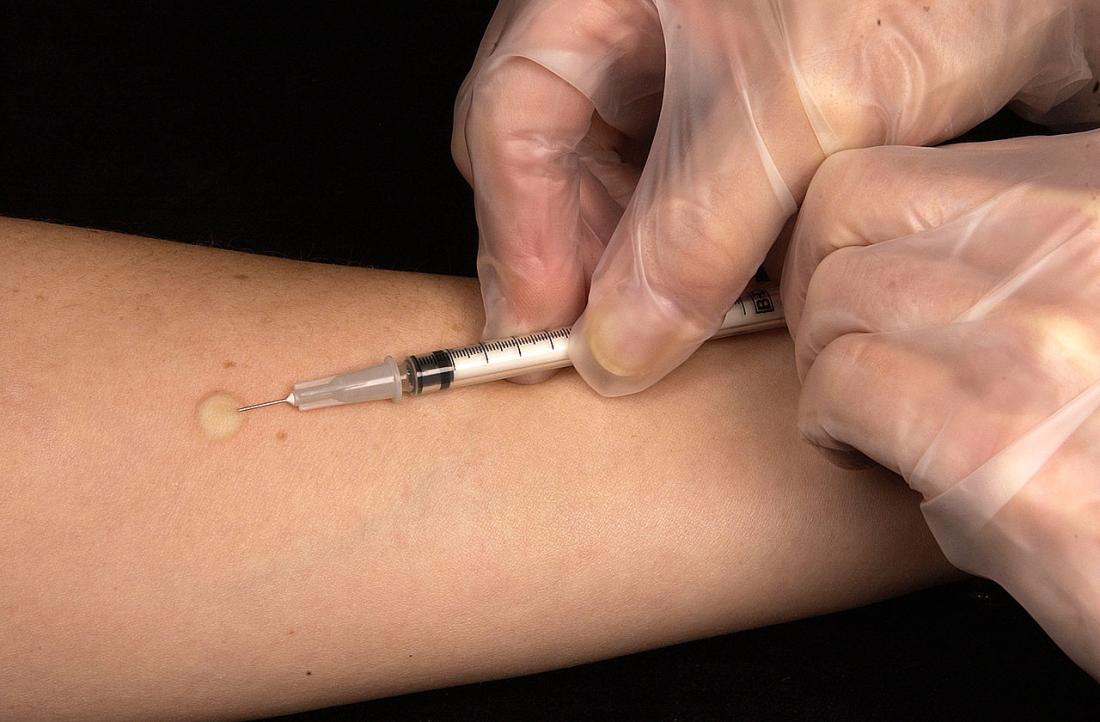
Step 1: First Tuberculin Skin Test
- Use a 27-gauge needle and tuberculin syringe for the injection. Inject 0.1 mL of purified protein derivative (PPD) intradermally into the inner forearm, forming a small, raised wheal (6–10 mm in diameter).
- Instruct the patient not to scratch or cover the injection site. The site should be observed and measured after 48 to 72 hours.
- After 48 to 72 hours, measure the diameter of induration (not redness) at the injection site using a transparent ruler.
- Record the result in millimeters (mm).
- Positive Result: Induration size indicates exposure or infection:
- ≥5 mm for high-risk individuals (e.g., immunocompromised, close TB contacts).
- ≥10 mm for moderate-risk individuals (e.g., healthcare workers, recent immigrants).
- ≥15 mm for low-risk individuals.
- Negative Result: No induration or induration less than the cut-off based on risk category.
- Positive Result: Induration size indicates exposure or infection:
Step 2: Second Tuberculin Skin Test
- If the first test is negative, administer a second TB skin test 1 to 3 weeks after the first test.
- Inject the same 0.1 mL of PPD intradermally in the opposite arm or a different site on the same arm.
- Similar to the first test, advise the patient not to scratch or cover the site.
- Measure and record the diameter of induration after 48 to 72 hours.
Result Interpretation
- Second Test Negative: No induration or induration less than the risk-based cut-off. The patient is considered uninfected.
- Second Test Positive: A positive reaction indicates a boosted immune response, suggesting past TB infection, not a new infection.
Important Notes
- Boosted Reactions are common in individuals who have received the BCG vaccine or had remote TB exposure.
- Annual Testing may be required for healthcare workers or those at continued risk.