Here you will learn about “Widal test procedure, principle, how to interpret it’s report”.
The Widal test, named after the French bacteriologist Georges-Fernand Widal.
It is a is a serological test widely employed for the diagnosis of typhoid fever and other related bacterial infections caused by Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi.
Widal test principle
The Widal test detects antibodies against O (outer membrane) and H (flagellar) antigens of Salmonella bacteria.
Elevated antibody levels indicate exposure to Salmonella typhi or Salmonella paratyphi, aiding in the diagnosis of diseases like typhoid fever.
Widal test slide method procedure
- Sample Collection: Blood samples are collected from the patient, usually during the acute and convalescent phases of the illness.
- Serum is separated from the blood, as it contains the antibodies that will be analyzed in the test.
- Preparation of Antigen Suspension: Cultures of Salmonella typhi and Salmonella paratyphi are grown, and their antigens are extracted and suspended.
- These antigen suspensions are then used in the subsequent steps of the Widal test.
- Serial dilutions of patient serum are mixed with the antigen suspensions on a microscope slide.
- Interpretation of Results: The results are interpreted based on the highest dilution of serum that shows visible agglutination. The agglutination reaction is observed for both O and H antigens.
A rising titer, meaning an increase in antibody levels between acute and convalescent samples, can strengthen the diagnostic accuracy.
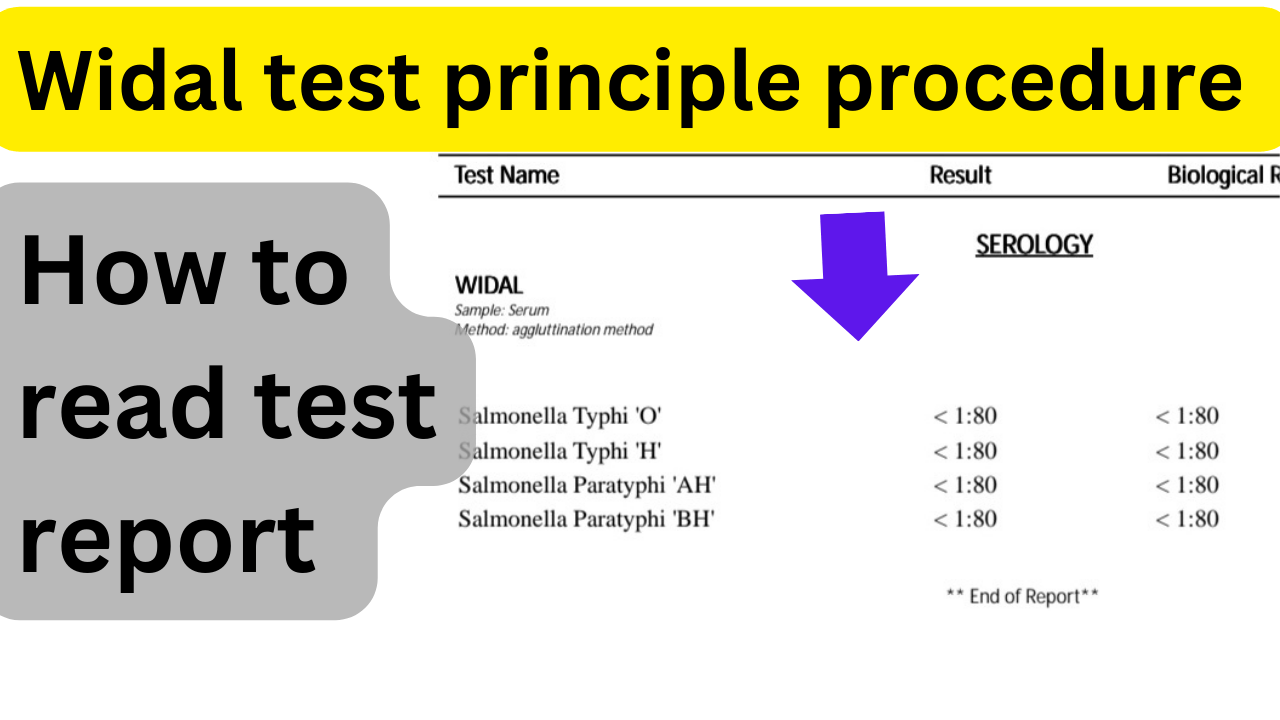
How to read widal test report
Interpreting Widal test results requires careful consideration of the agglutination patterns.
- Significant Titer Levels: Elevated titers (typically 1:160 or higher) for O and H antigens in the convalescent phase compared to the acute phase are indicative of recent or current infection.
- A fourfold or greater rise in titer between paired samples strengthens the diagnostic reliability.
NOTE: In regions where typhoid fever is endemic, individuals may have pre-existing antibodies due to previous exposure or vaccination. Hence, results should be interpreted cautiously, considering the patient’s history and clinical presentation.
I had learned how to do typhoid fever test and the difference between salmonella typhi and salmonella paratyphoid. It’s also educative.
Thank you for your valuable feedback.
I had learned how to do typhoid fever test and the difference between salmonella typhi and salmonella paratyphoid.
Thank you for your valuable feedback.