Glycolysis, a vitally essential metabolic pathway, plays a pivotal role occurring within the cytoplasm of cells. It serves as the foremost and primary step in efficiently breaking down glucose, which happens to be a fundamental and uncomplicated sugar molecule, ultimately resulting in the generation of ample energy.
This highly significant process holds paramount importance in facilitating both aerobic, oxygen-dependent respiration, and anaerobic, oxygen-independent respiration.
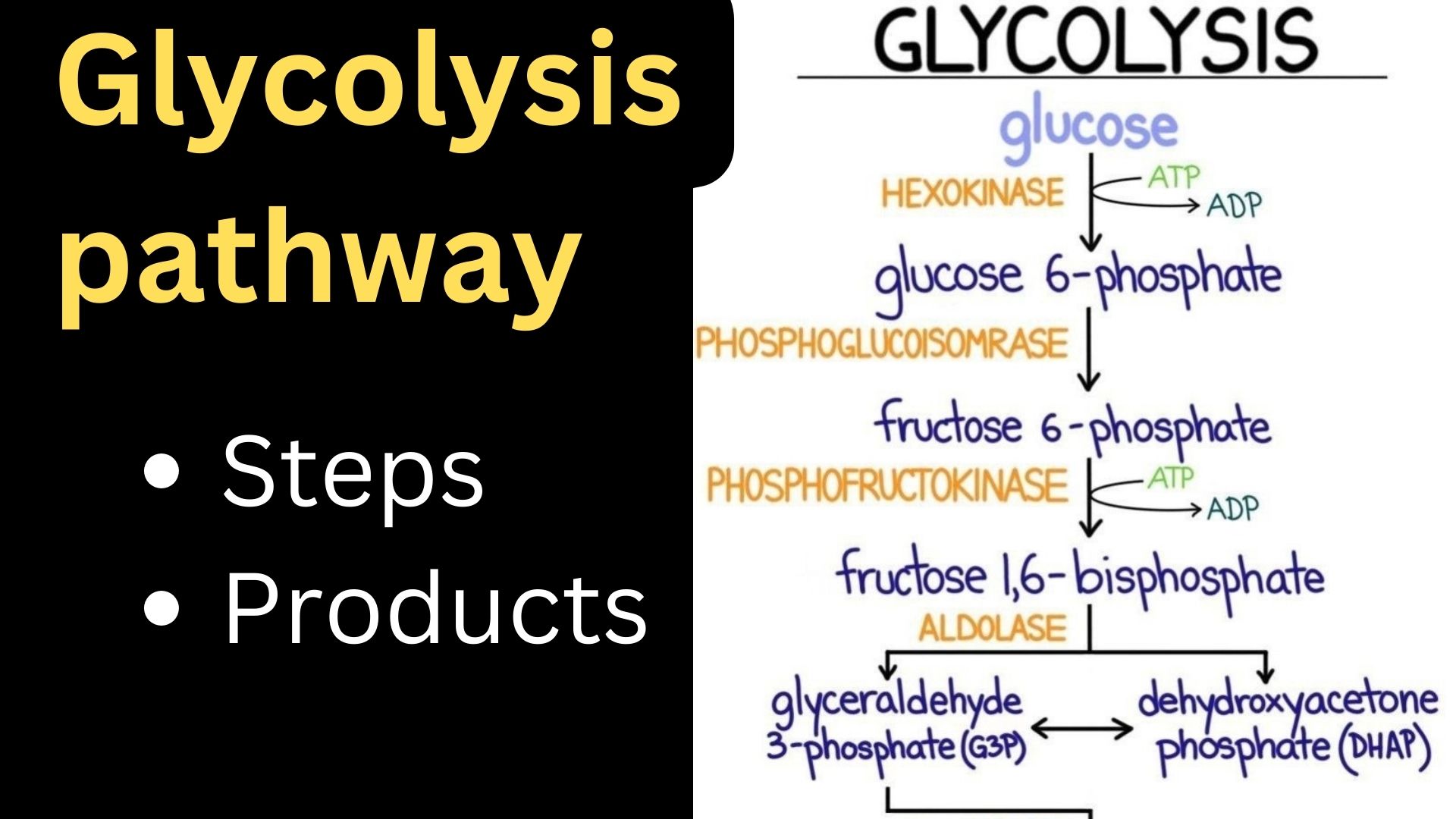
Steps of glycolysis with enzymes diagram
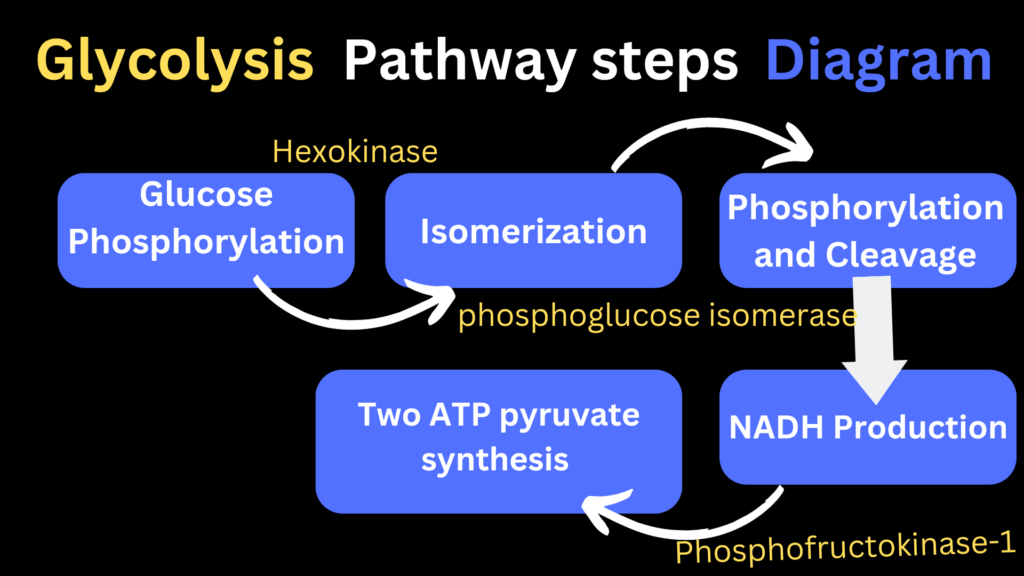
Certainly! Here are the steps of glycolysis:
Glucose phosphorylation: In the first step, a molecule of glucose is phosphorylated, which means it receives a phosphate group from ATP. This creates glucose-6-phosphate.
Isomerization: Glucose-6-phosphate is then rearranged and converted into its isomer, fructose-6-phosphate.
Second phosphorylation: Fructose-6-phosphate is phosphorylated again, this time with another ATP molecule. This forms fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
Cleavage: Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is cleaved into two three-carbon molecules called glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P).
Energy Harvesting and NADH Production: Each G3P molecule is oxidized and phosphorylated, resulting in the production of ATP and NADH. This converts G3P into 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
ATP Generation: 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate donates a high-energy phosphate group to ADP, forming ATP. This step also converts it into 3-phosphoglycerate.
Rearrangement: 3-phosphoglycerate undergoes an isomerization reaction to become 2-phosphoglycerate.
Dehydration: Water is removed from 2-phosphoglycerate, forming phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP).
Final ATP Generation: PEP transfers its phosphate group to ADP to form ATP, resulting in the formation of pyruvate.
- Note: The net production of ATP during glycolysis is 2 ATP molecules. However, it’s important to note that the gross production of ATP during glycolysis is actually 4 ATP molecules.
Here’s the video of “glycolysis pathway steps products diagram”.
Glycolysis pathway products
Glycolysis synthesis ATP, pyruvate and water molecules. Here’s the number of each product is.
- ATP : The net production of ATP during glycolysis is 2 ATP molecules.
- Pyruvate : Glycolysis produces two molecules of pyruvate.
- NADH: It generates two molecules of NADH.
- Water :Water molecules are not directly produced during glycolysis, but they can be formed as a byproduct of subsequent reactions in cellular respiration.
Quite interesting and educative
Thank you