Here you will learn about the Signs of HIV in CBC test.
A CBC (Complete Blood Count) test is a standard blood test that provides valuable information about a person’s overall health and can sometimes offer clues about certain medical conditions, including HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus).
While a CBC test alone cannot diagnose HIV, it can reveal certain abnormalities in the blood that may prompt further testing and investigation for the virus.
Here’s a detailed explanation of the signs of HIV that can be detected in a CBC test.
- Low CD4 T-Cell Count: HIV primarily attacks the immune system, particularly CD4 T-cells, which are a type of white blood cell. A CBC test can reveal a decrease in the absolute number of white blood cells (leukopenia) and specifically a low CD4 T-cell count.
- A lower-than-normal CD4 count may suggest a weakened immune system, which could be due to HIV infection.
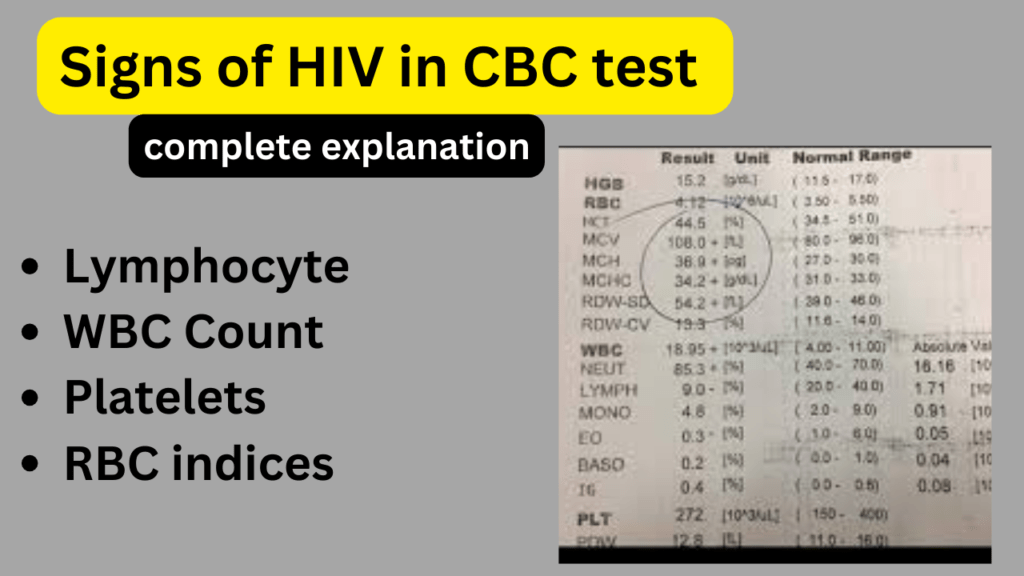
- Low Lymphocyte Count: Lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, play a crucial role in the immune system’s response to infections. In HIV-infected individuals, the lymphocyte count may be lower than normal.
- A CBC test measures both total lymphocyte count and lymphocyte percentages, and a consistent decrease in these values can be a sign of HIV.
- Anemia: HIV can lead to anemia, which is characterized by a low red blood cell count (RBC) or a decrease in hemoglobin levels. Anemia can cause symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and paleness. A CBC test can help identify anemia, and although it is a nonspecific finding, it may warrant further HIV testing.
- Low Platelet Count: HIV infection can sometimes lead to a decreased platelet count (thrombocytopenia), which can result in easy bruising and bleeding. A CBC test includes platelet count measurement, and a lower-than-normal count could be indicative of an HIV-related issue.
- Elevated White Blood Cell (WBC) Count: While HIV often leads to a decrease in CD4 T-cells and lymphocytes, it can sometimes cause an increase in the total white blood cell count (leukocytosis). This can be a sign of the body’s response to infection or inflammation.
- Abnormalities in Red Blood Cell Indices: A CBC test also provides information about red blood cell indices, such as mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC). Abnormal values in these indices can sometimes be associated with HIV-related complications or comorbidities.
NOTE: It’s important to note that while a CBC test can provide valuable information, it is not a definitive diagnostic test for HIV. HIV diagnosis typically requires specific blood tests, such as an HIV antibody test, HIV antigen/antibody test, or PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) test for viral RNA or DNA.