CRP test is an important biomarker of inflammatory cytokinesis such as interleukin-6. Therefore c-reactive blood test is used to assess their concentration.
It is classified as an acute-phase reactant, which means c-reactive protein concentration rises within a few hours. C-reactive protein increases in the following conditions,
- Cell injuries
- Infections
- Inflammation
C-reactive protein principle
This test is based on the latex agglutination method. It is slid agglutination method for qualitative and semi-quantitative analysis of c-reactive protein in the serum.
Latex particles coated with IgG anti-human CRP are agglutinated, when mixed with test serum, agglutination came within two to three minutes.
C-reactive protein test procedure
CRP test procedure consists of the following steps
- Centrifuge the test sample and separate the serum from other blood contents.
- Place one of each serum, test serum, positive control, and negative control in a circle.
- Now drop one drop of CRP latex reagent in each circle.
- Mix with a separate mixer or sticks.
- Tilt the slide back and forth slowly for two to three observing agglutination.
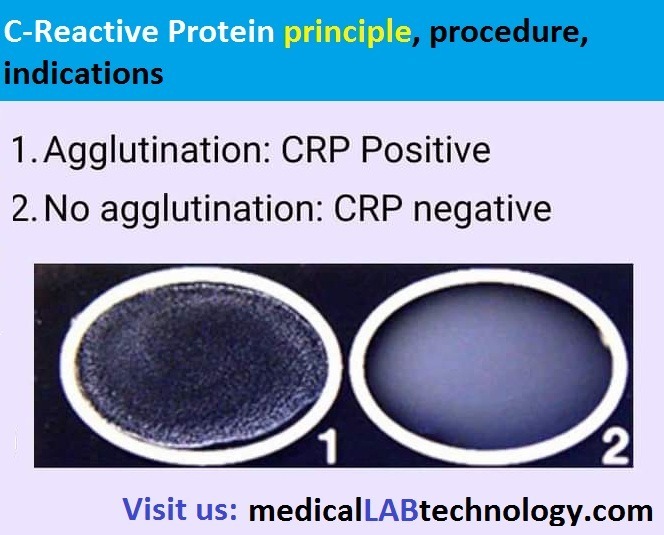
CRP test result interpretation
- POSITIVE RESULT: When the test sample shows agglutination after two minutes.
- NEGATIVE RESULT: When is no agglutination on the slide.
When Crp (C-reactive protein) test is high?
CRP is synthesized by the liver. When there will be any kind of infection or any kind of inflammation, CRP concentration will be high.